AWS MariaDB
SleakOps facilitates the integration of MariaDB databases through Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service). Amazon RDS for MariaDB is a fully managed service that simplifies database setup, operation, and scaling. MariaDB is a community-developed, commercially supported fork of the MySQL relational database management system, offering enhanced features and performance improvements. By leveraging SleakOps for this integration, you can efficiently manage MariaDB databases within your EKS environment, ensuring robust, scalable, and reliable data storage solutions for your applications.
FAQs
How does SleakOps manage MariaDB credentials?
When you create a MariaDB dependency in SleakOps, it automatically generates a Vargroup for your database. This Variable Group securely stores the MariaDB credentials and other important configuration details, such as the database endpoint and user access information. You'll be able to manage them from the Vargroups section.
What is Multi-AZ deployment and should I enable it?
Multi-AZ (Availability Zone) deployment ensures high availability and failover support by replicating your database in another availability zone. It's recommended for production environments to prevent downtime. Keep in mind that it increases costs.
Can I change the MariaDB version after the database is deployed?
Yes, MariaDB supports engine version upgrades. However, the upgrade process requires careful planning and may involve downtime. It's recommended to test the upgrade process in a non-production environment first.
What happens if I need more storage for my MariaDB database?
You can adjust the storage size when configuring your database. If you need more storage after deployment, SleakOps allows you to scale the storage size without downtime.
How do I create a MariaDB database dump?
To create a dump of your MariaDB database:
- Run the
mysqldumpCommand:
mysqldump -h MARIADB_ADDRESS -u MARIADB_USERNAME -p --all-databases > dump.sql
Replace MARIADB_ADDRESS, MARIADB_USERNAME, and dump.sql with the appropriate values.
- Consult Documentation: For more information on how to create a dump, refer to the official MariaDB documentation .
How do I import an existent dump using docker?
To import a database dump into your MariaDB RDS instance:
- Connect to the VPN: Ensure you are connected to the VPN of the AWS account where the RDS instance is located.
- Run Docker Container (Recommended):
- Install Docker on your local machine if not already installed.
- Run a MariaDB Docker container with the following command:
docker run -it --name mariadb-container -v ./initial_data/:/tmp/data/ -e MARIADB_ROOT_PASSWORD=MARIADB_PASSWORD -d mariadb bash- Attach to the container's terminal:
docker exec -t -i mariadb-container bash- Import the dump file:
Replacemysql -h MARIADB_ADDRESS -u MARIADB_USERNAME -p < /tmp/data/dump.sqlMARIADB_ADDRESS,MARIADB_USERNAME, anddump.sqlwith your specific details.
How do I import an existent dump to my local machine?
Alternatively, you can use a MariaDB client installed on your local machine to import the dump:
mysql -h MARIADB_ADDRESS -u MARIADB_USERNAME -p < dump.sql
What should I do if I encounter connection issues with my MariaDB database?
Check the following:
- Ensure the database endpoint, username, and password are correct.
- Verify that your security groups and firewall rules allow access.
- Ensure the database is running and has enough resources (CPU, memory). Otherwise, contact us.
AWS documentation: Amazon RDS MariaDB Documentation
Set up your MariaDB
1. Add MariaDB as a Dependency
To integrate MariaDB with SleakOps:
- In the SleakOps console, go to the "Dependencies" section
- Choose "MariaDB" from the list of available dependency types. For more detail see Dependencies: Integrating Databases, Caching, and Messaging Services.
2. Set up your MariaDB.
You will access the following form:
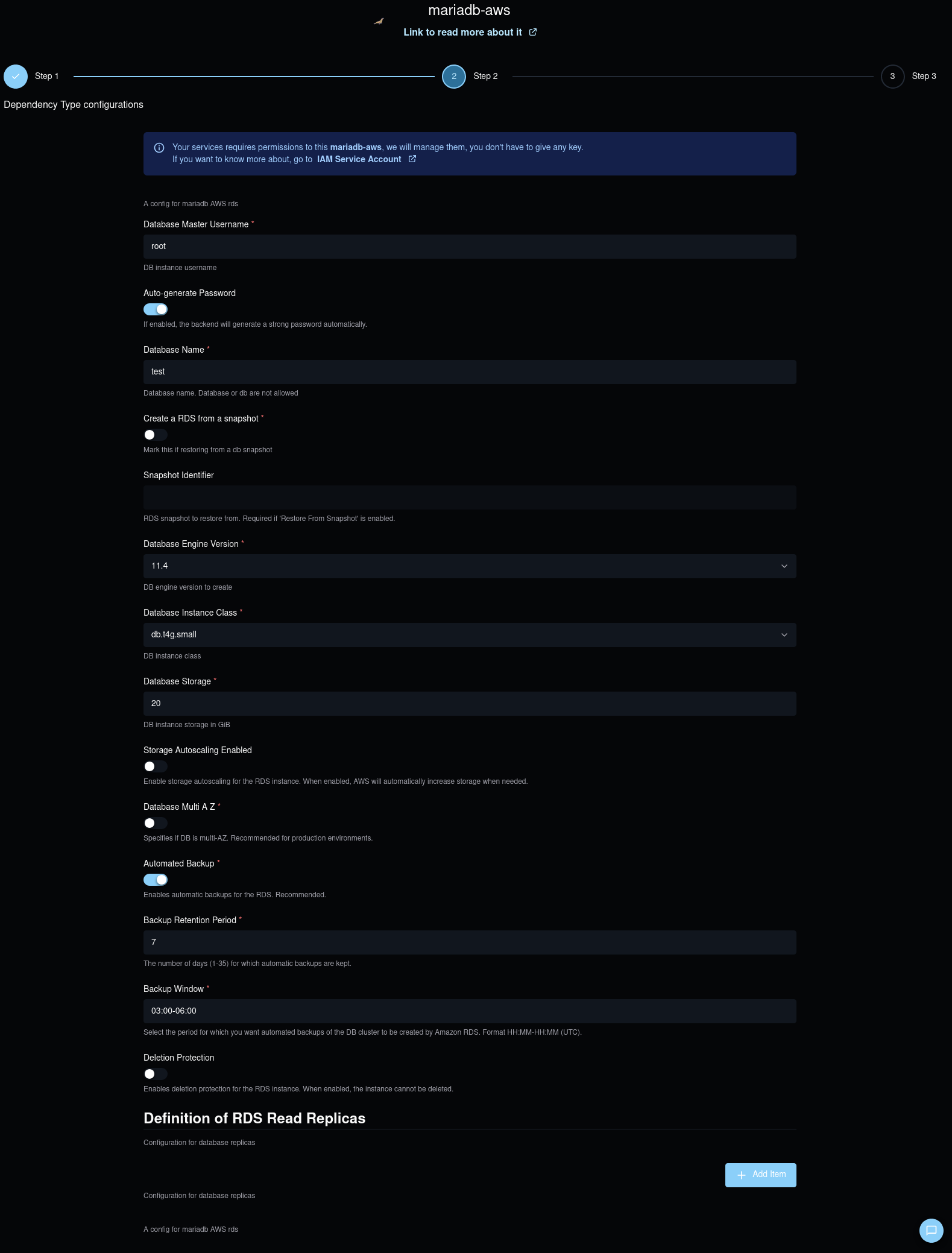
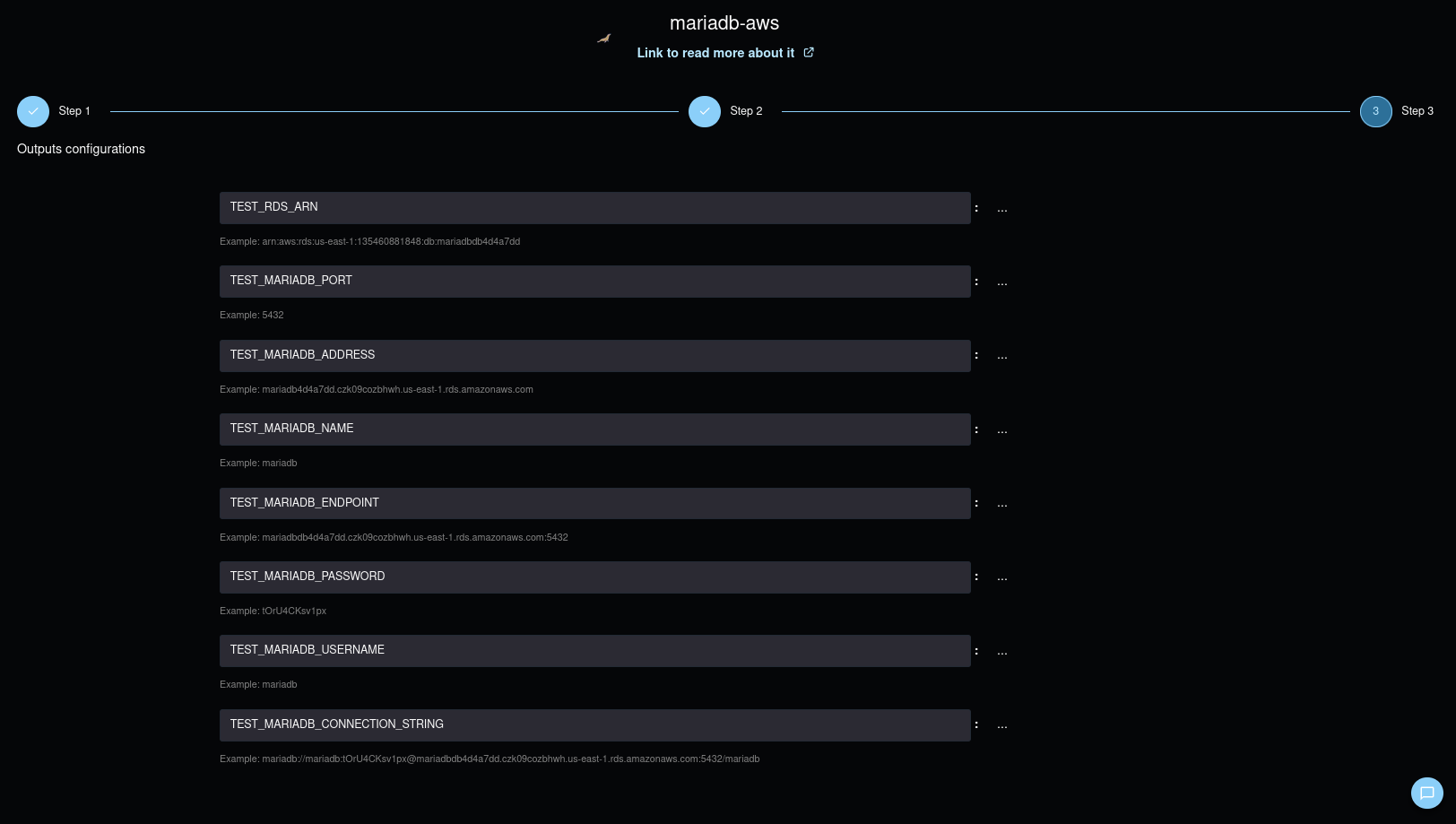
Here the parameters that SleakOps allows you to customize during the creation:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| Database Name | Name for the MariaDB database. Must follow pattern: lowercase letters and numbers, cannot be "db" or "database". This identifies your specific database within the MariaDB instance. |
| Database Engine Version | Select the specific version of the MariaDB database engine. Choose from versions supported. Each version includes specific MariaDB features, performance improvements, and security updates. |
| Database Master Username | Master username for the MariaDB database instance. This is the main user with administrative privileges. Cannot be "admin", "user", "database", or "name". Must start with a letter and contain only alphanumeric characters. |
| Auto-generate Password | If enabled, the backend will generate a strong password automatically for enhanced security. This is recommended for production environments to ensure password complexity. |
| Database Master Password | Password for the master user. Required if auto-generate is disabled. Must be at least 8 characters long and cannot contain @, ', ", or / characters. |
| Create a RDS from a snapshot | Mark this if restoring from a database snapshot. When enabled, you'll need to provide the snapshot identifier and some fields become read-only. |
| Snapshot Identifier | (Required if restoring from snapshot) RDS snapshot identifier to restore from. This allows you to restore your database from a previous backup point. |
| Database Instance Class | Define the instance class that specifies the hardware configuration for your MariaDB database. Choose from t4g/t3 (burstable performance) or m7i/m8g (memory optimized) instance types. This controls CPU, memory, and network performance. |
| Database Storage | Specify the amount of storage allocated for the database in GiB (20-6144 GB). MariaDB uses General Purpose SSD storage by default. This is the initial storage allocation for your database. |
| Storage Autoscaling Enabled | Enable automatic storage scaling for the RDS instance. When enabled, AWS will automatically increase storage when needed, up to the maximum allocated storage limit. |
| Maximum Allocated Storage | (Required if storage autoscaling is enabled) Maximum storage size in GiB (20-65536 GB) when storage autoscaling is enabled. This prevents unexpected costs by setting an upper limit for automatic scaling. |
| Database Multi-AZ | Enable Multi-Availability Zone deployment for high availability. This creates a standby replica in a different AZ and provides automatic failover capability. Recommended for production environments. |
| Automated Backup | Enable automatic backups for the RDS instance. When enabled, MariaDB will perform daily snapshots and transaction log backups, providing point-in-time recovery capabilities. |
| Backup Retention Period | (Required if automated backup is enabled) Number of days (1-35) for which automatic backups are kept. Longer retention periods provide more recovery options but increase storage costs. |
| Backup Window | (Required if automated backup is enabled) Time period for automated backups in HH:MM-HH:MM format (UTC). Choose a time when your database activity is typically low to minimize performance impact. |
| Read Replicas | (Required if automated backup is enabled) Configuration for database read replicas to improve read performance and provide additional availability. Each replica requires a name, instance class, and publicly accessible setting. |
3. Customize your variable's name for your MariaDB database.
As explained, when a dependency is created, SleakOps generates a vargroup to hold all the needed attributes. In this step you can change the name of the attributes in case it is needed. SleakOps completes the values automatically. After this step, your dependency is created.