Connect your Git Account
To leverage the full power of SleakOps, you'll need to connect your Git account to our platform. This connection allows SleakOps to access your repositories, enabling seamless integration, automated deployments, and efficient management of your codebases
SleakOps supports integration with the following Git providers:
- Github
- GitLab (including self-hosted instances)
- Bitbucket
FAQs
Can I connect more than one Git Account?
Not allowed yet.
How do I Connect my account?
Access the Setting >> Autorizations section in SleakOps. Select your provider and grant access to SleakOps. See steps below.
Can I change my Git Account?
Yes, you can do it by deleting de existing one and connecting the new one. Be sure the new account has access to the projects using in SleakOps.
How do I disconnect an account?
By clicking in the X button next to the git provider. Consider that current projects will continue to function but won't be able to receive updates once this integration is removed.
If you're using GitHub, you will also need to remove the Sleakops app from your GitHub account to complete the deletion process.
Set up your git Account
1. Navigate to the git authorization section
Into the Left Pane, access the Settings option and then, click on Authorizations.
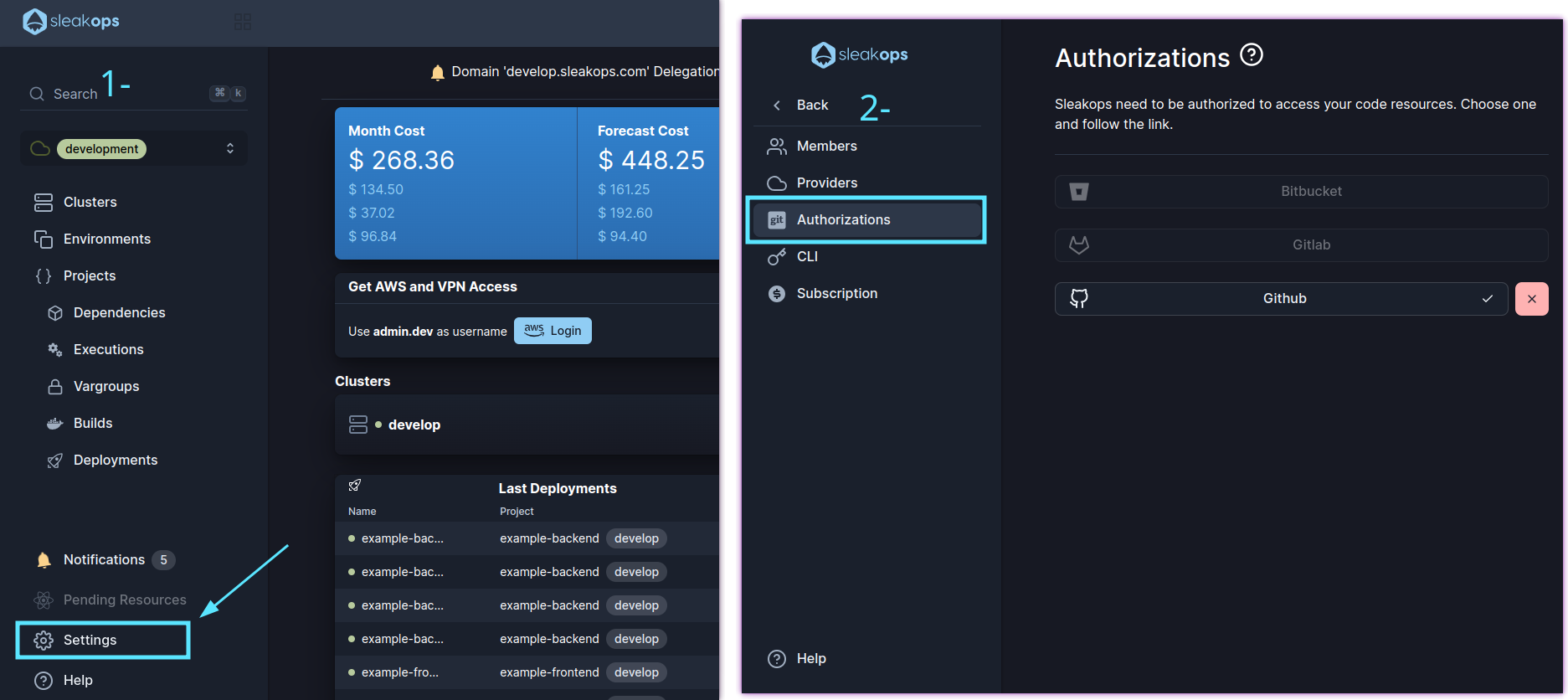
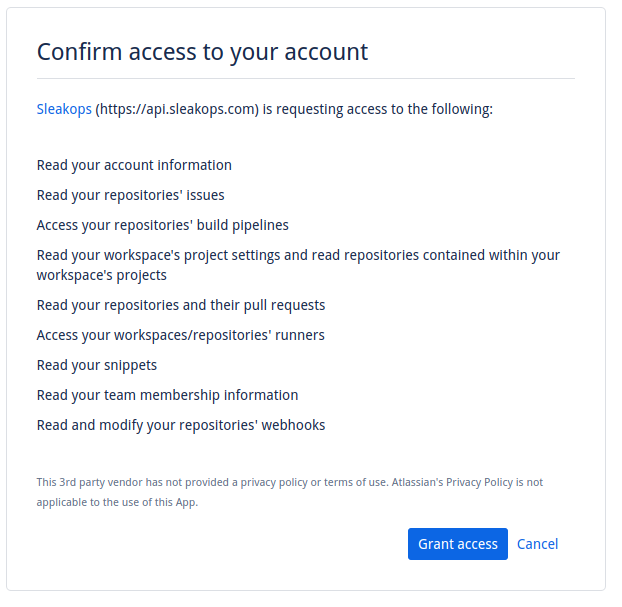
2. Select your Git provider and grant access to SleakOps
Click on your provider an follow the required steps for each one in order to grant access.
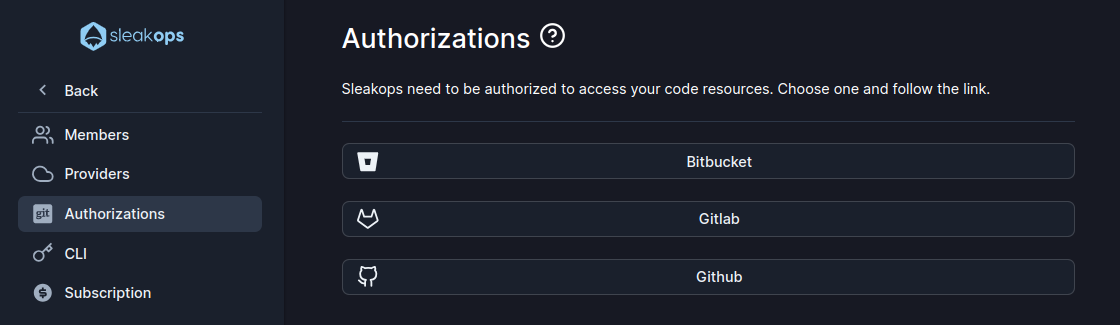
Integrations
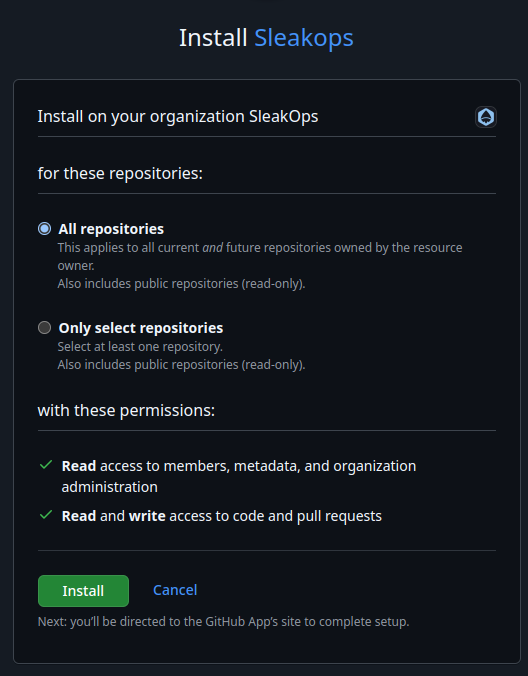
Github
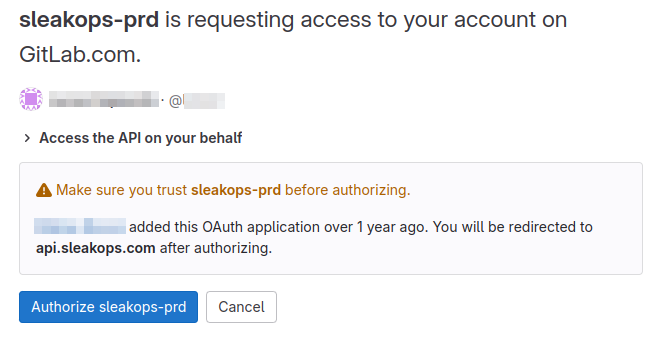
Gitlab
Bitbucket
Self-Hosted GitLab
Connecting a self-hosted GitLab instance requires creating an OAuth application in your GitLab installation, as each self-hosted instance has a unique URL and authentication system.
Prerequisites
- Administrator access to your self-hosted GitLab instance
- Your GitLab instance must be accessible from the internet (SleakOps needs to communicate with it)
- HTTPS is strongly recommended for security
Step 1: Create an OAuth Application in Your GitLab Instance
-
Access the Applications page
- Navigate to your GitLab instance:
https://yourgitlab.com/-/profile/applications - Or go to: User Settings → Applications
- Navigate to your GitLab instance:
-
Create a new application
- Click "Add new application" or "New application"
- Fill in the following information:
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Name | SleakOps (or any descriptive name) |
| Redirect URI | https://api.sleakops.com/api/integrations/self-gitlab/callback/ |
| Scopes | Select api and offline_access (required for persistent access and automatic token renewal) |
The Redirect URI must be exactly as shown below (including the trailing slash):
https://api.sleakops.com/api/integrations/self-gitlab/callback/
Do not modify this URL.
- Save the application
- Click "Save application" or "Submit"
- You will be shown two important values:
- Application ID (Client ID)
- Secret (Client Secret)
Copy both the Application ID and Secret immediately. The Secret will only be shown once and cannot be retrieved later.
Store these credentials securely. If you lose the Secret, you'll need to regenerate the OAuth application.
Step 2: Connect Your Self-Hosted GitLab to SleakOps
-
Navigate to SleakOps Authorizations
- Log in to your SleakOps account
- Go to Settings → Authorizations
-
Select Self-Hosted GitLab
- Click on "Self-Hosted GitLab" integration option
-
Enter your OAuth application details
- GitLab Instance URL: Enter your GitLab instance URL (e.g.,
https://gitlab.yourcompany.com)- Do not include a trailing slash
- Must start with
http://orhttps://
- Application ID: Paste the Application ID from Step 1
- Application Secret: Paste the Secret from Step 1
- GitLab Instance URL: Enter your GitLab instance URL (e.g.,
-
Authorize SleakOps
- Click "Connect" or "Authorize"
- You will be redirected to your GitLab instance
- Review the permissions and click "Authorize"
- You will be redirected back to SleakOps
-
Verify the connection
- Once redirected, you should see your self-hosted GitLab account listed as connected
- You can now select repositories from your self-hosted GitLab instance when creating projects
What permissions does SleakOps need?
SleakOps requires two scopes:
api scope grants the following permissions:
- Read repository information and file contents
- Create and manage branches
- Create and update files (for automated deployments)
- Create merge requests
- Access commit information
offline_access scope allows SleakOps to:
- Obtain a refresh token for long-term access
- Automatically renew expired access tokens
- Maintain persistent connection without requiring re-authorization
Without offline_access, the access token will expire after ~2 hours and the integration will break until manually re-authorized.
These permissions are required for SleakOps to clone your repositories, build container images, deploy applications, and manage infrastructure-as-code.
Troubleshooting
Connection fails with "Invalid URL" error
- Ensure your GitLab instance URL does not end with a trailing slash
- Verify the URL starts with
http://orhttps:// - Example: ✅
https://gitlab.company.com❌https://gitlab.company.com/
Authorization redirects but connection fails
- Verify the Redirect URI in your GitLab OAuth application matches exactly:
https://api.sleakops.com/api/integrations/self-gitlab/callback/ - Check that the Application ID and Secret are correct
- Ensure both
apiandoffline_accessscopes were selected when creating the OAuth application
Network/Firewall issues
- Ensure your self-hosted GitLab instance is accessible from SleakOps servers
- If your GitLab is behind a firewall, you may need to whitelist SleakOps IP addresses
- Contact SleakOps support for IP whitelist information
SSL/Certificate errors
- Self-signed certificates may cause connection issues
- Use a valid SSL certificate from a trusted certificate authority
- Ensure your GitLab instance has proper HTTPS configuration