Node Pools
A node pool is essentially a collection of nodes within a Kubernetes cluster that have similar configurations, such as the same machine type, operating system, and instance size.
All nodes in a node pool are configured identically, making it easier to manage and maintain consistency across your cluster. This is especially useful when scaling the cluster, as additional nodes added to the pool will have the same specifications.
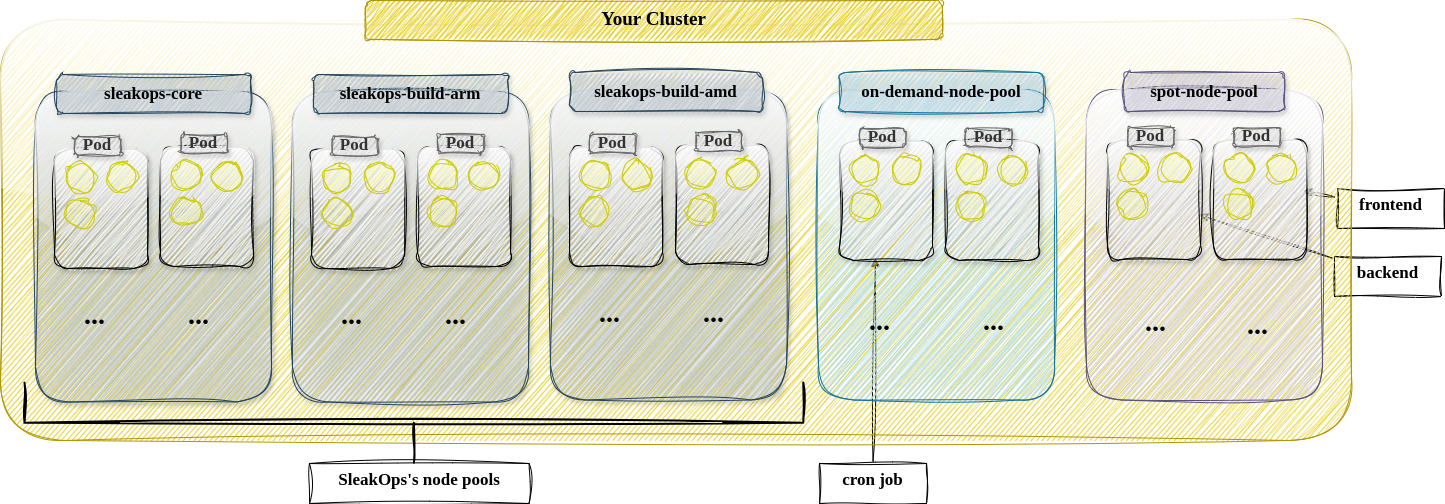
When a Cluster is created on SleakOps, a set of node pools are created, based on the architecture type you’ve selected during the cluster selection.
- sleakops-build-arm64 & sleakops-build-amd64: A default ones to run properly your builds. They can’t be edited or deleted.
- sleakops-core: Ensures the scalability of the critical components and cluster addons.
- ondemand-arm/amd: Ready for you to use.
- spot-arm/amd: Ready for you to use.
Do not delete manually the following node pools: sleakops-build-arm64, sleakops-build-amd64, sleakops-core.
FAQs
What are the different kind of node pools?
-
Reserved: are instances that you commit to using for a specific term (1 or 3 years) in exchange for significant cost savings (up to 75% less than On-Demand pricing). They provide the best price with commitment and are ideal for:
- Predictable Workloads: Applications with steady, predictable usage patterns that can benefit from long-term commitment.
- Production Environments: Critical applications that require guaranteed capacity and cost optimization.
- Cost Optimization: Workloads where you can commit to usage for extended periods to maximize savings.
-
Spot: are instances that take advantage of spare capacity in a cloud provider's data center, offering up to 90% cost savings compared to On-Demand instances. While they can be terminated if the provider needs capacity back, this is not a limitation but an opportunity for well-architected applications. Ideal for:
- Cloud-Native Applications: Applications designed with stateless architecture that can handle pod interruptions and restart quickly.
- Cost-Optimized Workloads: Perfect for applications where significant cost savings (up to 90%) outweigh the need for guaranteed capacity.
- Resilient Systems: Applications with proper health checks, graceful shutdowns, and automatic restart capabilities.
-
On-Demand: are instances in a Kubernetes cluster that run with a fixed pricing model, providing reliable access to compute resources without the risk of interruption. Can be used:
- Critical Workloads: Applications that require consistent uptime, such as databases, financial systems, or other critical services.
- Long-Running Tasks: Tasks that cannot be interrupted without significant consequence.
Priority Order: When you select multiple node types, the system will automatically prioritize them in the following order to optimize costs: Reserved (best price with commitment) → Spot (best price without commitment) → On-Demand (highest price but most flexible).
For detailed guidance on choosing the right instance types and evaluating application compatibility, see Instance Types and Node Management.
How many Node Pools can I have?
SleakOps base plan, allows you to have three extra node pool besides the build ones. If you need more, contact us.
Can I convert a spot node pool into an on demand and viceversa?
You can't directly convert a Spot node pool into an On-Demand node pool or vice versa, but you can achieve the desired outcome through a series of steps in SleakOps. Here’s how you can transition between node pools types:
- Create a Node Pool of the new desired type.
- Updade your workloads and projects to run into the new Node Pool.
- Delete the old node pool if it is not longer needed.
Can I convert a ARM node pool into an X86 and viceversa?
You can't change the architect type of a node pool, but you can achieve the desired outcome through a series of steps in SleakOps. Here’s how you can transition between node pools architectures:
- Create a Node Pool of the new desired architecture.
- Update your workloads and projects to run into the new Node Pool.
- Delete the old node pool if it is not longer needed.
How do I create a Node Pool?
Follow Creating a Node Pool
How do I manage my a Node Pool?
Follow Managing a Node Pool